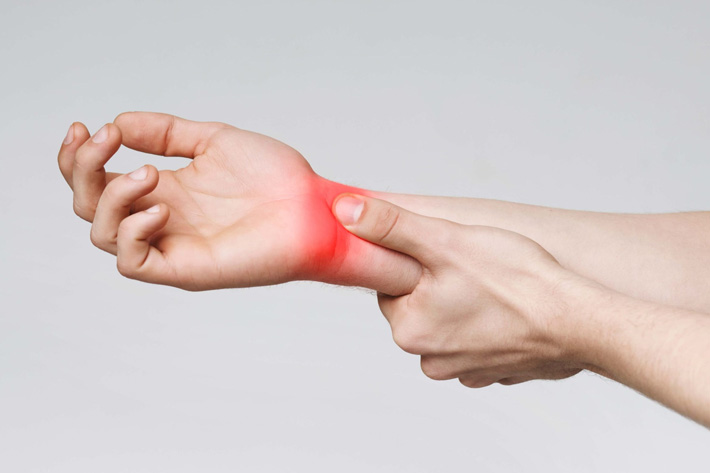
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects the hand and wrist. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand through a narrow passageway called the carpal tunnel, becomes compressed or irritated. This compression can lead to pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
Treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Here are some common approaches:
1. Non-surgical treatments:
- Wrist splinting: Wearing a splint or brace that holds the wrist in a neutral position can help relieve pressure on the median nerve.
- Activity modification: Avoiding activities that may worsen symptoms or applying ergonomic principles to reduce strain on the wrist.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
2. Physical therapy:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises for the wrist and hand can improve flexibility and reduce symptoms.
- Ultrasound therapy and wrist mobilization techniques may be used to relieve pain and improve function.
3. Corticosteroid injections:
- In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered into the carpal tunnel to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief.
4. Surgery:
- Carpal tunnel release surgery may be recommended if symptoms are severe or do not improve with conservative treatments.
- There are two types of surgery: open carpal tunnel release, where a small incision is made in the palm, and endoscopic carpal tunnel release, where a tiny camera and instruments are inserted through small incisions.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss the most suitable treatment options based on your specific situation. They will consider factors such as the severity of symptoms, duration of symptoms, and your overall health before recommending a course of action.