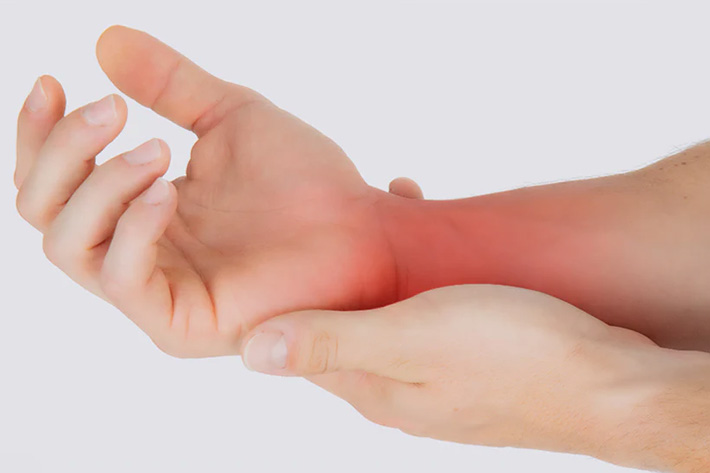
Tendinitis of the wrist tendons, also known as wrist tendonitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the tendons in the wrist. The tendons are fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones, allowing for joint movement. Wrist tendonitis commonly affects the tendons surrounding the wrist joint, such as the extensor and flexor tendons.
Causes:
- Repetitive motions: Activities that involve repetitive wrist movements, such as typing, using a computer mouse, playing musical instruments, or sports like tennis, can strain the tendons over time.
- Overuse or excessive force: Engaging in activities that require forceful or prolonged wrist movements, such as weightlifting or manual labor, can lead to tendonitis.
- Poor ergonomics: Incorrect wrist positioning while performing tasks, such as typing with improper wrist posture, can contribute to the development of tendonitis.
- Age-related factors: Tendons tend to become less flexible and more prone to injury with age, increasing the risk of tendonitis.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Wrist tendonitis typically causes pain in the affected wrist. The pain may be sharp, dull, or throbbing and can worsen with wrist movements or activities.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the tendons may result in localized swelling around the wrist area.
- Tenderness: The affected tendons may be tender to touch or pressure.
- Reduced range of motion: Tendonitis can lead to stiffness or limited movement in the wrist joint.
- Weakness: In some cases, weakness in the wrist or difficulty gripping objects may occur.
Treatment and Management:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms and giving the wrist adequate rest is crucial for healing. Immobilizing the wrist with a splint or brace may be recommended.
- Ice and heat therapy: Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain. Heat therapy, such as warm compresses, may be beneficial for promoting blood flow and relaxation.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises and stretches to strengthen the wrist muscles and improve flexibility. They may also employ techniques like ultrasound or electrical stimulation for pain relief.
- Ergonomic modifications: Adjusting your workstation setup, using ergonomic tools, and maintaining proper wrist posture during activities can help prevent further strain on the tendons.
- Corticosteroid injections: In severe cases, a healthcare professional may administer corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is rare and typically reserved for cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific situation. They can assess your symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and provide personalized recommendations to manage and treat wrist tendonitis.