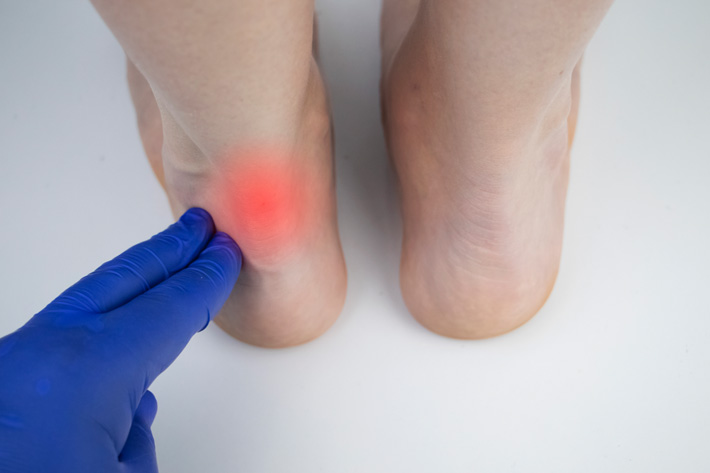
Achilles tendinitis refers to the inflammation and irritation of the Achilles tendon, which is the large tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and non-insertional. The causes and treatment strategies for each type differ slightly. Let’s explore them in more detail:
1. Insertional Achilles Tendinitis:
Causes: Insertional Achilles tendinitis occurs when the tendon becomes inflamed near its attachment to the heel bone (calcaneus). It can be caused by repetitive stress, overuse, or degeneration of the tendon. It may also be associated with a bone spur at the site of insertion.
Treatment Strategies:
- Rest: Avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms and give the tendon time to heal.
- Ice: Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, to reduce inflammation.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Specific exercises and stretches can help strengthen the calf muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce stress on the tendon.
- Orthotic devices: Wearing heel lifts or orthotic shoe inserts can help relieve pressure on the Achilles tendon.
- Night splints: Wearing a splint at night can help stretch the calf and Achilles tendon while sleeping.
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT): This non-invasive treatment uses shockwaves to stimulate healing and reduce pain.
- Surgical intervention: If conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered to remove the bone spur and repair the damaged tendon.
2. Non-Insertional Achilles Tendinitis:
Causes: Non-insertional Achilles tendinitis occurs when the middle portion of the tendon degenerates and develops small tears. It is commonly associated with repetitive activities and overuse injuries.
Treatment Strategies:
- Rest: Give the tendon adequate rest to allow for healing and prevent further damage.
- Ice: Apply ice to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain.
- NSAIDs: Over-the-counter NSAIDs can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the calf muscles and improve flexibility.
- Eccentric exercises: Specific exercises that involve lengthening the Achilles tendon while under load can promote healing and improve tendon strength.
- Orthotic devices: Wearing appropriate footwear or using orthotic inserts can help provide support and reduce stress on the tendon.Extracorporeal shockwave therapy: ESWT may be used to stimulate healing and reduce pain.
- Surgical intervention: If conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms, surgery may be recommended to remove damaged tissue or repair the tendon.
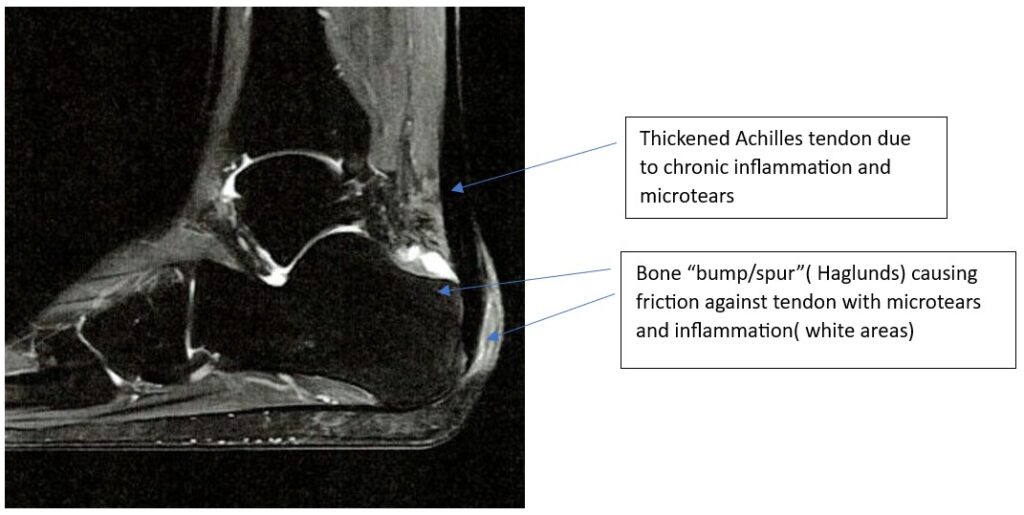
It’s important to note that treatment approaches may vary depending on the severity of the condition, individual factors, and the recommendations of a healthcare professional. If you suspect you have achilles tendinitis, it’s best to consult with us for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.